MacBook's Journey to Linux - Part 3: My little fairies
linux Debian terminal Estimated reading time: 1 minuteConfiguration of the system requires a lot of actions and tasks. Without a terminal, this can quickly become a nightmare.
Here, I just want to note a list of very useful commands, that can be used by everyone. Part of them are available on Mac, but some - are only for Linux.
Related articles:
- MacBook’s Journey to Linux - Part 1: Hello world!
- MacBook’s Journey to Linux - Part 2: Bring the light!
- MacBook’s Journey to Linux - Part 3: My little fairies
- MacBook’s Journey to Linux - Part 4: Speak to me.
My little fairies
Below I noted just the most used commands by myself.
This is not a comprehensive guide or some cheat sheet.
| Dirs | |
|---|---|
| Current | pwd |
| Change directory | cd dir |
| Go up | cd .. |
| Make dir | mkdir dir |
| List files | ls |
| Process/Service | |
| Show snapshot of processes | ps |
| Show real-time processes | top |
| Kill process with id pid | kill -9 PID |
| Find by name | pgrep -f <path to the service> |
| Status | systemctl status <name> |
| Stop/Start service | systemctl stop <name> and systemctl start <name> |
| File | |
| Mode GOD ;] | chmod 777 file |
| Permission to read/write | chmod 600 <file> |
| File owner | chown user:group <file> |
| PCKG | |
| Search pckg | dpkg -l | grep <name> |
sudo ldconfig -p | grep <name> |
|
| List by pattern | sudo locate <name> |
| Search in dirs | find -iname <name>* //partial name |
| Archive | |
| Unpack | tar xzf <name>.tgz |
| Pack | gzip file.txt |
| Transfer | |
| Copy a file to a server directory securely using the Linux scp command. | scp [source_file] [user]@[remote_host]:[destination_path] |
| Synchronize the contents of a directory with a backup directory using the rsync command. | rsync -a [source_directory] [user]@[remote_host]:[destination_directory] |
Few other notes
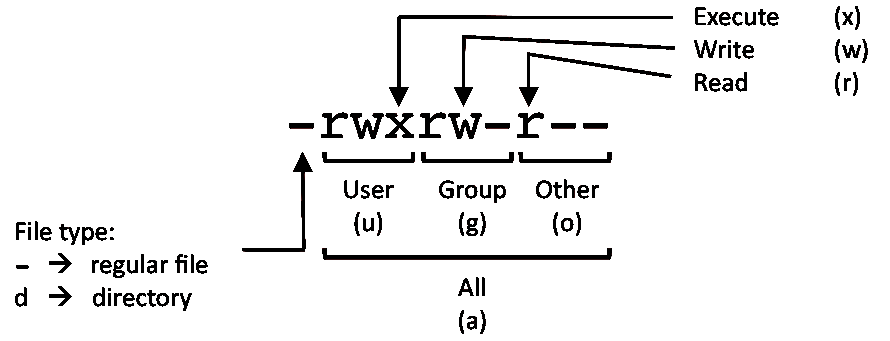
- Permission code
The first digit is owner permission, the second is group, and the third is everyone. Calculate permission digits by adding the numbers below.
Example
4 - read (r)
2 - write (w)
1 - execute (x)
rwx rwx rwx chmod 777 filename
rw- — — chmod 600 filename
- Nano shortcut
Read - Ctrl-R
Save - Ctrl-O
Close - Ctrl-X
Resources
« MacBook's Journey to Linux - Part 2: Bring the light!
BeagleBone® Blue - initial config via serial port »
Share on: